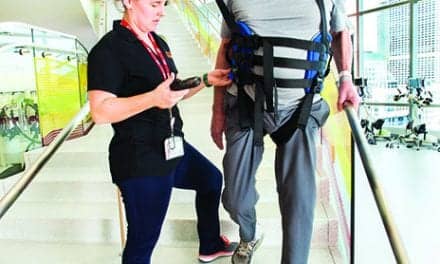
CORBYS reportedly integrates the use of physiological data such as heart rate, temperature, and muscle activity measurements to provide feedback to the therapist and control the robot. Researchers report that the technology aims to assist patients by creating a system comprised of a powered orthosis to help move the legs and a mobile platform providing patient mobility.
“The walking robot has several settings, and the therapist selects the correct mode based on how far the patient has come in his or her rehabilitation,” Anders Liverud, ICT researchers, SINTEF, explains.
Sensors are first attached to the patient’s body prior to requesting the patient to walk on a treadmill. The therapist manually corrects the walking pattern and uses the sensors to create a model of the patient’s walking patterns, Liverud adds. Next, the system is designed to adjust the walking pattern to the defined model and new adjustments are made to improve the walking pattern. Patients are fitted with an EEF cap to measure brain activity and by using “these signals combined with input from other physiological and system sensors, the robotic system registers whether the patient wants to stop, change speed or turn, and can adapt immediately,” Liverud says.
The release notes that the patient’s freedom to decide how and where they would like to walk offers control and motivation to continue training during rehabilitation, while the robot continues to correct any walking pattern errors.
For more information on the CORBYS project, click here.
[Photo Credit: III: CORBYS]
[Source: SINTEF]